TAPI Pipeline
- Afghanistan is set to start work on the long-awaited Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India (TAPI) pipeline, a landmark project worth USD 10 billion and committed to enhancing regional energy connectivity and boosting economic growth.
- This development has been possible after years of delay mainly due to security concerns in Afghanistan.
TAPI pipeline:
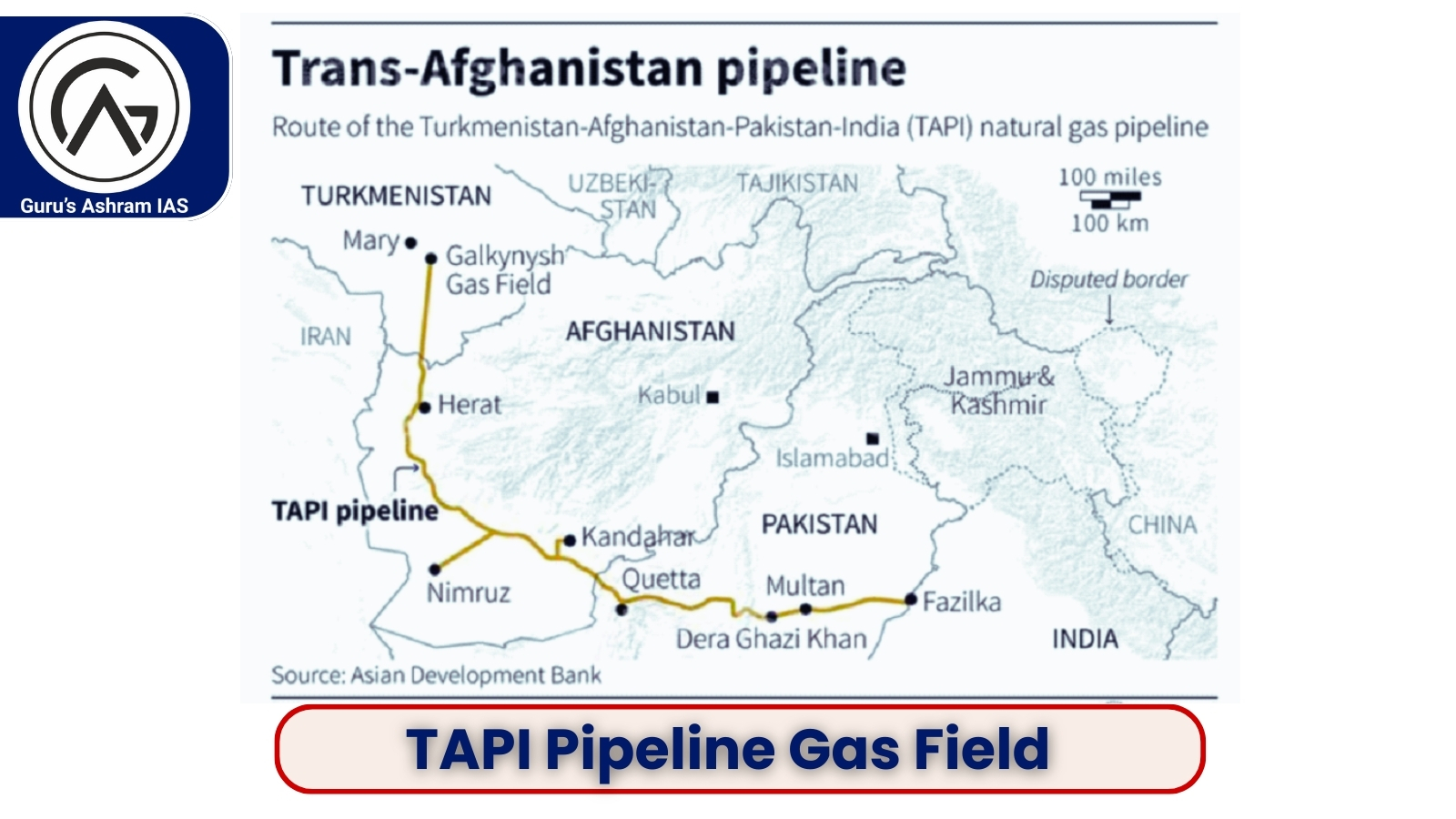
- The TAPI pipeline is a major infrastructure project designed to transport natural gas from Turkmenistan’s Galkynysh gas field through Afghanistan, Pakistan and India.
- The pipeline will be about 1,814 km long and is expected to deliver about 33 billion cubic metres (BCM) of natural gas per annum.
- During its 30-year operational period it will supply gas to Afghanistan (5%) Pakistan (47.5%) and India (47.5%).
- This pipeline is also known as’ Peace Pipeline ‘due to its potential to promote regional cooperation and stability.
- The project began in the 1990s, with significant progress made in 2003 with the support of the Asian Development Bank (ADB). India joined the project in 2008, which was a major milestone in its development.
- TAPI Pipeline Company Limited (TPCL) is responsible for the construction and operation of this pipeline. The company is a joint venture between Turkmenistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan and India, each of which has a stake in the project.
Importance:
The environmental impacts:
- This pipeline provides an important alternative to coal, which reduces carbon dioxide emissions compared to coal-based energy production.
- For India, which is heavily dependent on coal, TAPI can facilitate the transition to clean energy sources and help meet its ambitious emission reduction targets (net-zero emission targets).
- The TAPI pipeline can help reduce the problem of air pollution in major cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Karachi and Islamabad by providing clean energy options.
Economic benefits:
- In addition to energy supply, the pipeline could provide opportunities for economic development in Afghanistan and Pakistan through transit fees and job creation. It can also promote investment in renewable energy sources in these countries.
The strategic impact:
- TAPI is an important component of the wider geopolitical competition for influence in Central Asia. The US views the pipeline as a strategic rival to the Iran-Pakistan-India (IPI) pipeline, which is backed by Iran and Russia.
- For Turkmenistan, TAPI presents an opportunity to diversify its export markets and reduce dependence on existing routes to China and Russia.
- China’s investment in the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) highlights the competitive nature of energy infrastructure projects in the region. TAPI can act as a counter to Chinese influence, especially in Pakistan.
- The pipeline enhances cooperation between Central and South Asian countries and promotes cooperation in energy, communications and transportation.
- For India, the pipeline establishes Turkmenistan as an important energy partner, which will enhance India’s connectivity with Central Asia. This is in line with India’s comprehensive strategy to improve regional connectivity and energy security.
Challenges related to TAPI pipeline:
Security concerns:
- Most of the pipeline will pass through Afghanistan, which is known for its challenges such as political instability and humanitarian crisis. Ensuring smooth implementation of the project has been a recurring issue.
Finance and Administration:
- Getting adequate financing remains a major hurdle. The Asian Development Fund is expected to receive a small portion, while the remaining amount will be received from private investors.
- In addition, the administration of the pipeline has become complex due to the partnership of four different pipeline companies (one for each partner country).
The investment climate:
- Turkmenistan’s closed economy and limited integration into the global market pose significant barriers to attracting investment. Corruption and governance issues further complicate the investment landscape.
India vs Pakistan:
- India’s own disputes with Pakistan raise questions about its long-term commitment to the TAPI pipeline. Political tensions between the two countries could hinder cooperation and smooth operation of the project.
Concerns about the environment:
- Although natural gas is cleaner than coal (natural gas emits 50 to 60% less CO2 than the coal used in the plant, by comparison) it still has environmental problems.
- The extraction and transportation of natural gas involves risks such as water and soil pollution and the possibility of earthquakes due to fracking.
Solutions:
- Alternative financing sources such as private sector investment, international financial institutions and government grants need to be explored in addition to the Asian Development Fund.
- Tax exemptions, subsidies and other incentives should be provided to attract foreign investment. A clear and stable regulatory framework will also boost investor confidence.
- There is a need to promote industrial development along the pipeline route to generate employment, generate economic activity and diversify regional economies.
- Regional security cooperation should be strengthened to address common issues and ensure the safety of the pipeline. A central coordination body needs to be set up to oversee the project so as to ensure orderly decision making and efficient management.
- Positive relationships with local communities along the pipeline route should be maintained to gain their support and minimize safety risks.
- Best practices for natural gas extraction and transportation should be implemented to minimize environmental impact and prevent pollution.